What is Chainlink?
Chainlink addresses a major problem of the Ethereum Blockchain ecosystem. In spite of the fact that with the technology of Smart Contracts practically every problem can be represented by programming, since Ethereum’s programming language Solidity is “Turing complete”, there is no possibility to establish a native communication with external systems. This significantly limits the potential and applications of the Ethereum Blockchain.
Chainlink has found a solution for this, the so-called “Oracles”. They establish a connection to the “outside world” by enabling access to external data. Thus, Chainlink technology offers any external programming interface (API) access to Smart Contracts that were previously isolated on the blockchain and had no access to external data.
Source: https://chain.link/features/
Oracles, however, are not a new invention of the Chainlink development team, but can already be found in the blockchains of Aeternity and Qtum. So far, however, oracles have been centralised services. This means that every smart contract that uses an external service has a single point of failure.
However, this destroys all the advantages resulting from the decentralised character of Smart Contracts. The solution is decentralized oracles developed by Chainlink. Thus the security and determinism of the blockchain and smart contracts can be combined with external data.
The Single Point of Failure Problem
Basically Smart Contracts create a completely new and revolutionary form for agreements of any kind. While classic contracts are easy to manipulate and break, smart contracts are deterministic. This means that the contractual agreements are always adhered to and executed as programmed in the contract.
This is guaranteed by the cryptographic technologies of the blockchain. This possibility offers a revolutionary potential. Especially in fraud-prone industries, such as insurance, international trade and finance, Smart Contracts can provide more justice and transparency.
The use of a single Oracle (= external data feeds), however, fundamentally destroys the reliability of the Smart Contract with a single point of failure. As ordinary oracles are third party services with a centralized checkpoint, the decentralized consensus mechanism of the blockchain is undermined. The operator of a data feed could manipulate the data and thus destroy the determinism of the smart contract.
In the worst case scenario, Oracle can even be operated by one of the parties involved in the transaction. The usual solution in today’s world, the involvement of an authority, i.e. a “Single Trusted Third Party” – an entity with a high level of trust – is also not a solution. This approach runs counter to the principles of the blockchain, according to which a consensus is always formed dezentral.
End-to-End Reliability for Smart Contracts
The aim of the Chainlink network is therefore to connect smart contracts with oracles that are reliable end-to-end and cannot be manipulated. Chainlink’s approach to the problem is a decentralized computing.
The Chainlink network allows multiple independent nodes to perform distributed calculations about the accuracy of an external input before it is written to a smart contract. Thus, Chainlink’s decentralized Oracle network offers the same security guarantees as the blockchain itself. The prerequisite for this is that there are several sources that provide the same data, such as the prices of cryptocurrencies: CoinMarketCap, CryptoCompare and Brave NewCoin Insights.
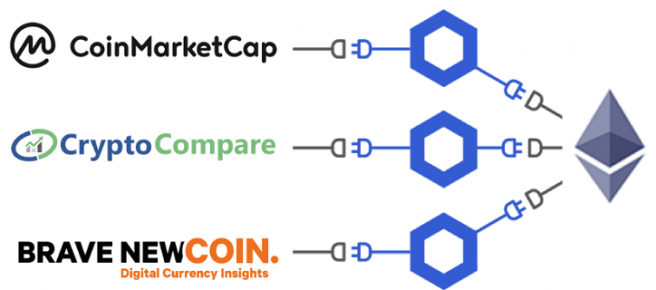
Source: https://blog.chain.link/chainlink-live-ethereum-mainnet-connected-consensus/
Chainlink creates a decentralized Oracle network that has all the tools to create any type of Oracle design pattern for Smart Contracts. The Chainlink software acts as an Oracle as well as a flexible framework to support Smart Contract developers.
The network consists of Chainlink nodes, each providing its own data feed, API or other external data source. In order to motivate the data suppliers to provide information, they are paid in LINK tokens. Basically, it should be possible for anyone who has external data to pass it on directly to the blockchain in exchange for LINK tokens.
How does the Chainlink network work in detail?
An essential idea of Chainlink technology is that the data provided by an Oracle is authenticated before it is passed on to a Smart Contract. An important component for evaluating the authenticity of external data is the Chainlink Oracle reputation system.
The rating system works similar to Amazon or Ebay. With Chainlink, however, the reputation is based on a large number of key figures, e.g. availability, response time and successfully completed orders. Technically, the Chainlink network consists of an on-chain and an off-chain component that communicate with each other to provide the service. The on-chain component consists of Smart Contracts implemented on the Ethereum blockchain.
These are Oracle Contracts that process data requests from users who want to access external data. You filter the data queries. As soon as the network receives a request, the Chainlink network converts it into an internal contract (3 individual contracts).
The contracts are responsible for linking the requesting contract with a suitable Oracle. In addition, the data is collected on-chain according to the query, the results are evaluated and the final result is calculated, which is provided to the Smart Contract. The 3 individual contracts each have the following tasks:
- The reputation contract checks the reliability of the oracle against the reputation system.
- An order matching contract captures the data request in the network and accepts the appropriate offers from the Oracle suppliers.
- The aggregating contract collects the data from the selected oracles, evaluates it and summarizes it into a final result. This step is extremely important to ensure the integrity of the external data and to prevent manipulation.
The off-chain component of the network, on the other hand, is responsible for collecting the external data. It consists of Oracle nodes connected to the Ethereum network. The received data is processed by the Chainlink Core software, which is operated by each node in the network. It is responsible for the interaction between the off-chain infrastructure and the blockchain.
What is the LINK token used for?
The LINK token is an ERC677 token that takes over the functionality of the ERC20 token standard. It is used to pay node operators for retrieving data for Smart Contracts.
It is important to know that the LINK token is permanently operated on the Ethereum Mainnet. Unlike other projects (like EOS or Tron) that hosted their token on the Ethereum Blockchain until the Mainnet launch, Chainlink will always remain part of the Ethereum Mainnet. Accordingly, there will be no token swap.
The Initial Coin Offering (ICO) from LINK
The Initial Coin Offering of Chainlink (LINK) took place in September 2017. A total of 350 million LINK tokens worth 32 million US dollars were sold. This represents 35 percent of LINK’s total offering, which amounts to 1 billion tokens. The distribution of the LINK tokens looks as follows:
- 350 million LINK tokens sold in crowdsale
- 350 million LINK tokens are earmarked for node operators to promote the Chainlink ecosystem.
- 300 million LINK tokens went to the company behind Chainlink for development.
As of August 2019, there are only 350 million LINK tokens in circulation, which were sold during the crowdsales.
The Google Cloud uses Chainlink
In June 2019, Google announced in a blog post that the tech giant is working on a project that uses Chainlink. Google wrote in detail that they were working on applications that would store cloud-generated data on a blockchain.
To integrate the external data into the blockchain the Google project Chainlink uses. The data is retrieved from the company’s own data warehouse BigQuery and written to the Ethereum blockchain via the Chainlink oracles. Thanks to Google’s announcement, the LINK price rose by more than 30 percent in June 2019 in a single day.
Further Chainlink Partnerships
Chainlink has an impressive list of partners. Key partners include SWIFT, Google, Oracle, Gartner and IC3. In addition to Google, SWIFT in particular is a big name whose technology links over 11,000 financial institutions worldwide.

Source: https://chain.link/
Which wallet is suitable for LINK?
Basically, any wallet that supports ERC20 tokens is suitable for LINK. Our top recommendation for ERC20 tokens is the MyEtherWallet. If you want to know exactly how to set up and use the wallet, we recommend our wallet guides.
Conclusion: Is Chainlink (LINK) worth an investment?
From our point of view Chainlink can be a very interesting investment. It is the first and currently only blockchain project that tries to close the gap between Smart Contracts and the real world with decentralized oracles.
In contrast to the competition, the oracles that Chainlink uses are decentralized. LINK is the cryptocurrency that drives the network. Thus, the LINK price could benefit greatly if Chainlink becomes established and finds its way into the mainstream. Whether the partnerships mean far-reaching use cases in reality for Chainlink, however, remains to be seen.
Subscribe to our daily newsletter!
No spam, no lies, only insights. You can unsubscribe at any time.
If you are interested in investing in Chainlink (LINK), we recommend that you read our guide, how to buy Chainlink. We explain how to invest in LINK quickly and easily.
[ratings]




